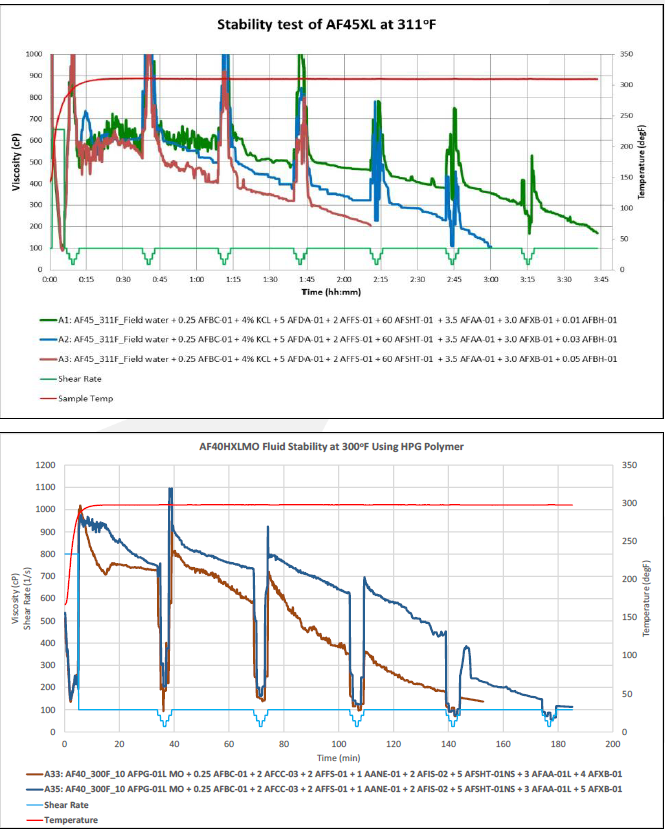
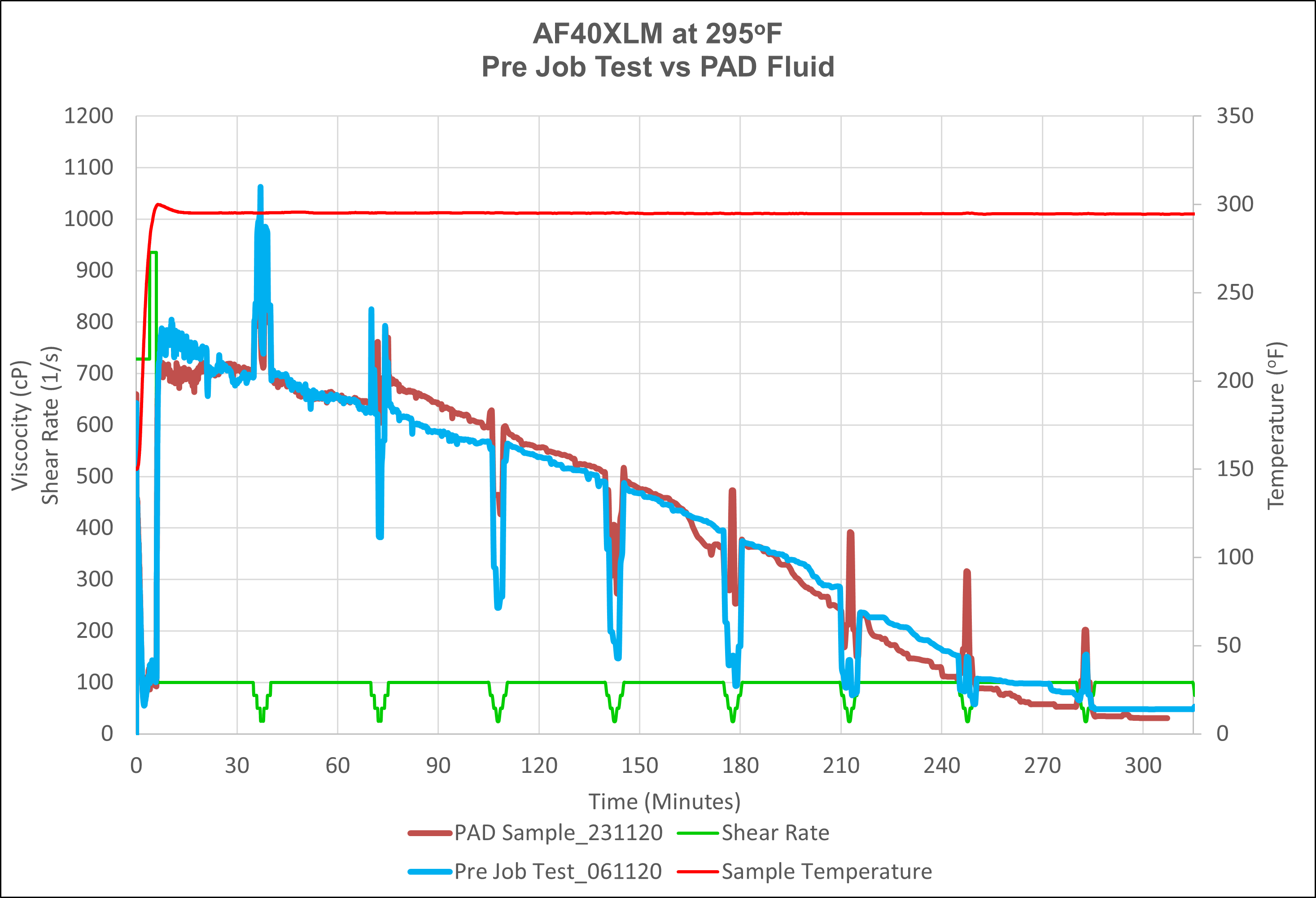
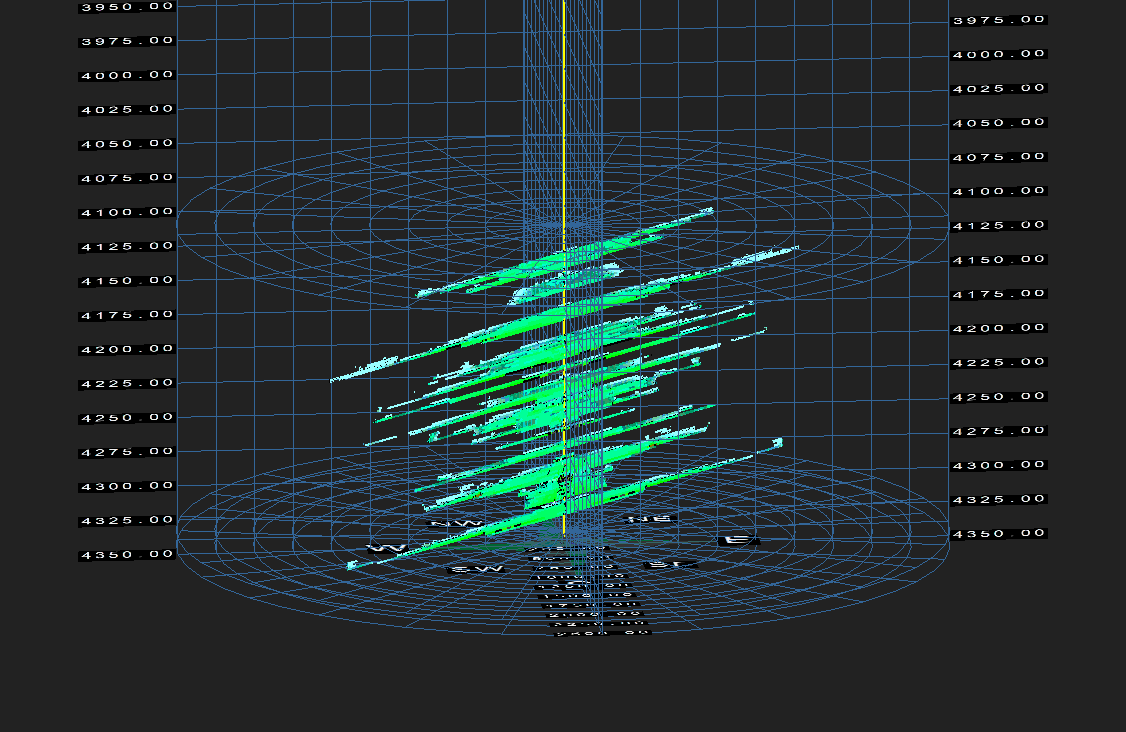
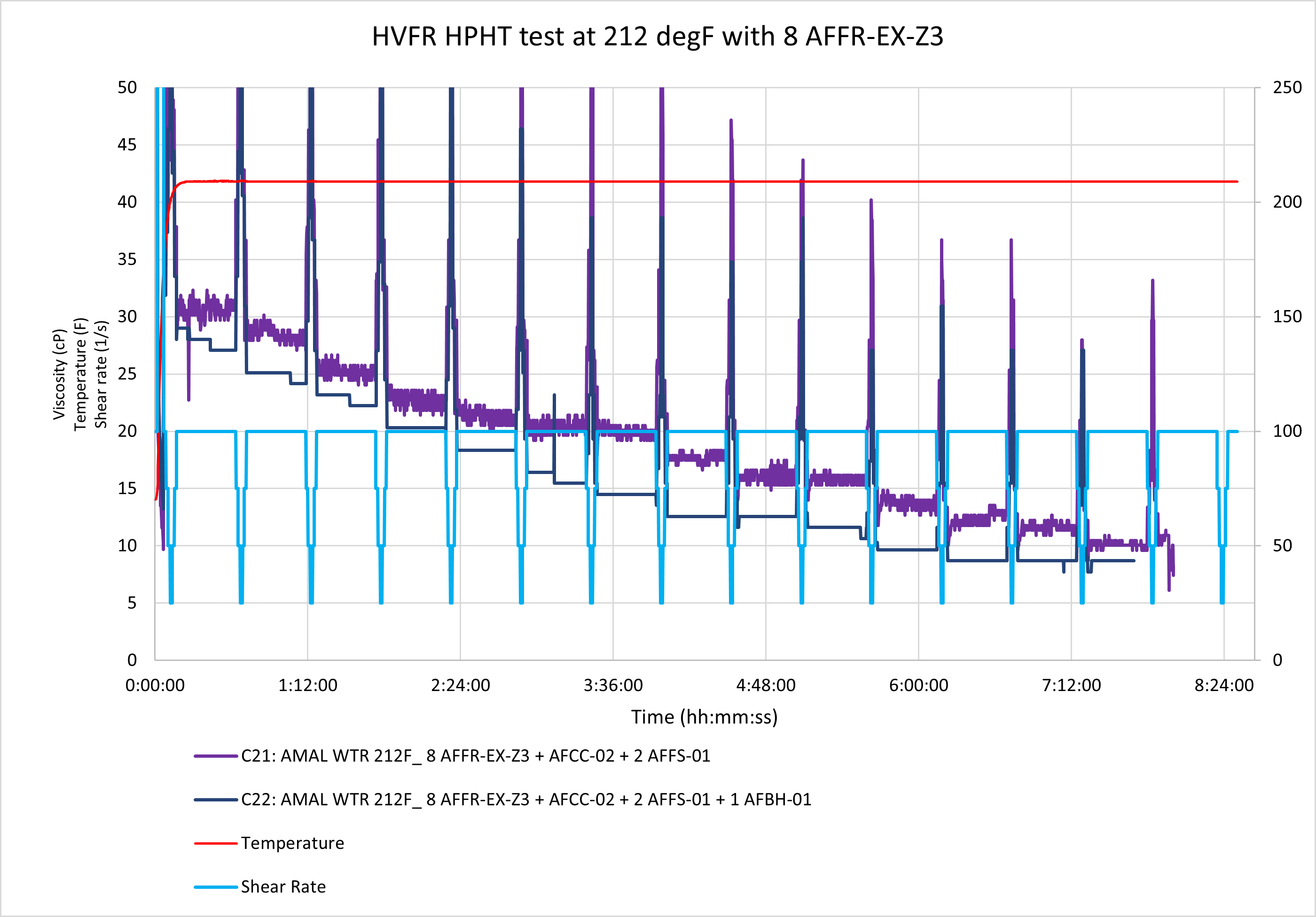
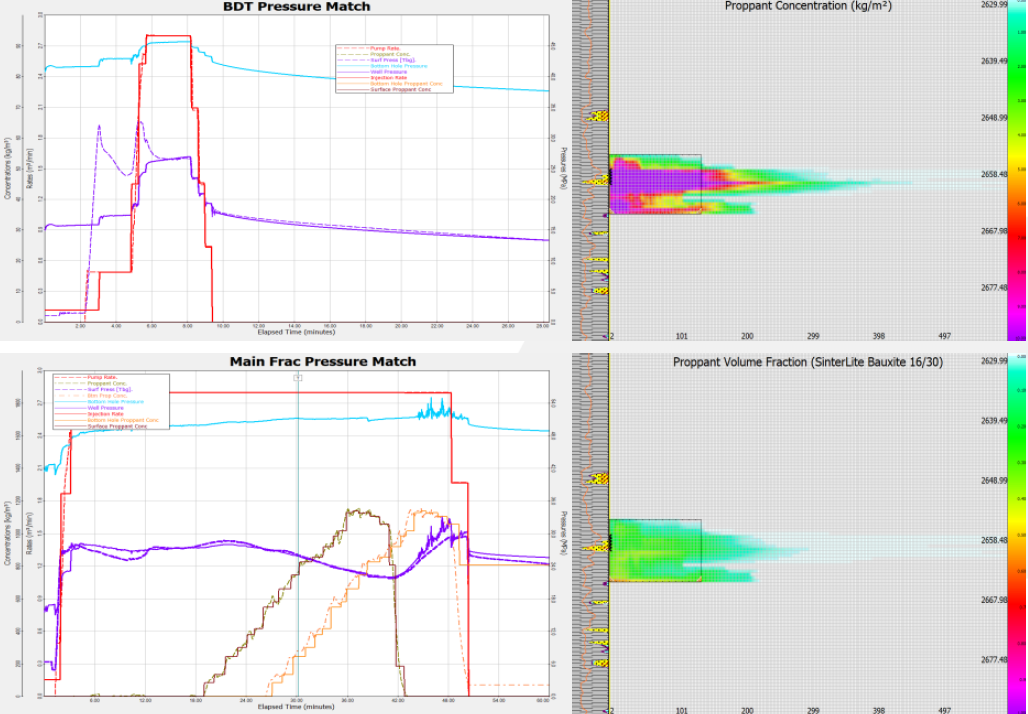
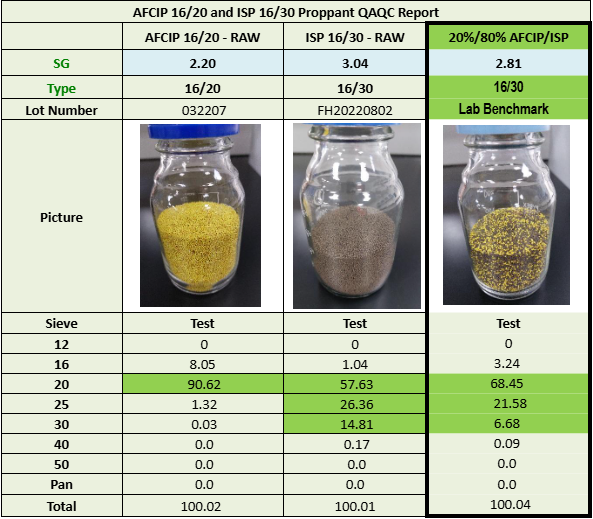
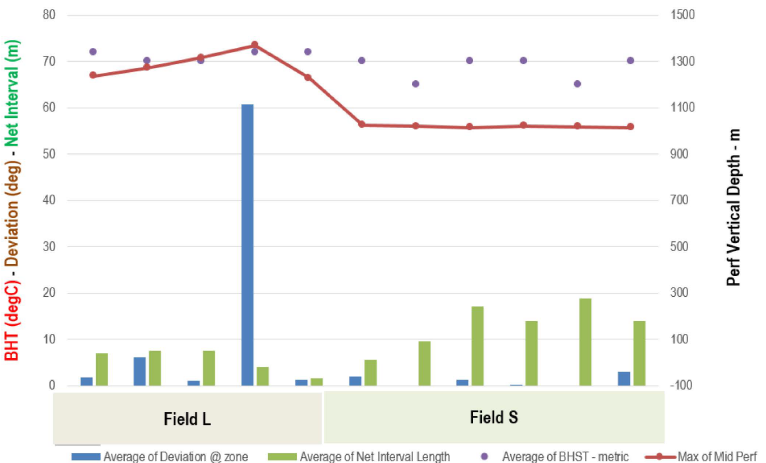
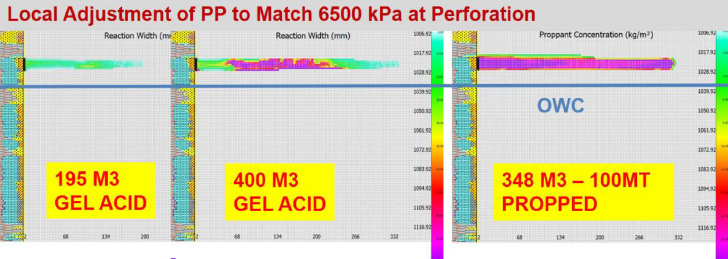
Post Fracture Evaluation
Master databases were collected to include critical information:
- Well & reservoir data
- Design & actual treatment parameter
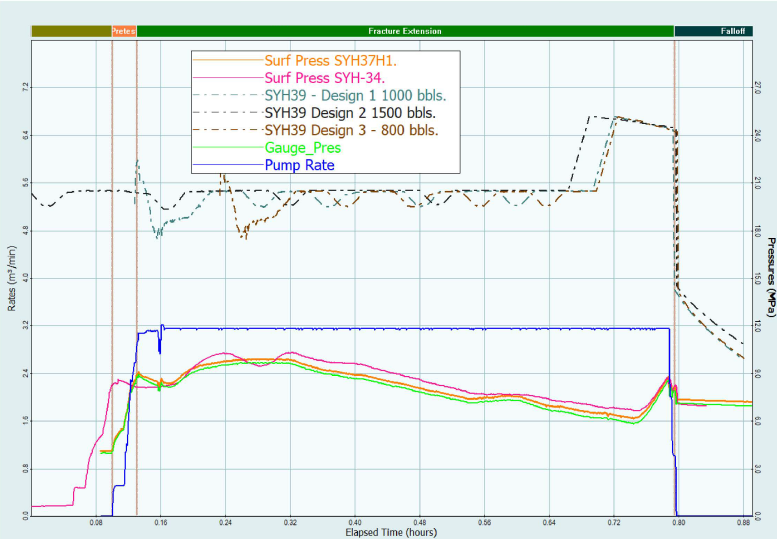
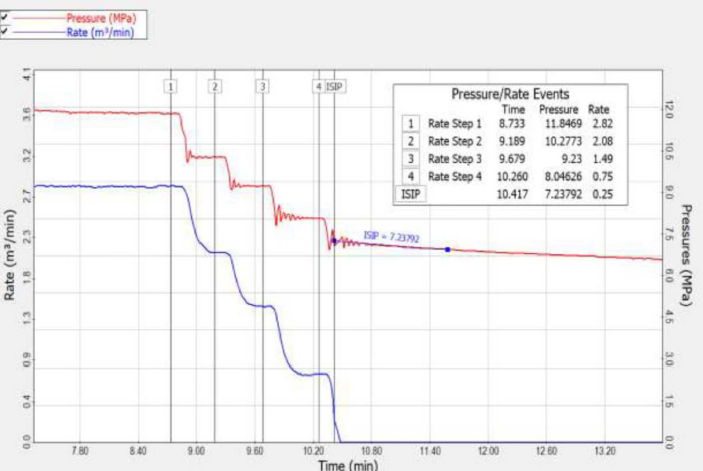
- Pressure, rate data and diagnostics
- Other operational parameter
Following the fracturing campaign:
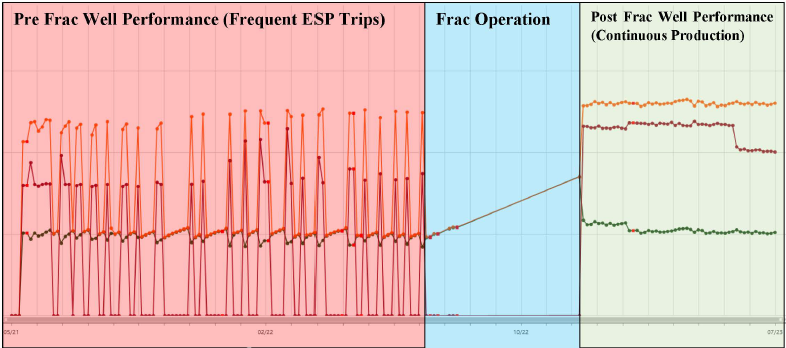
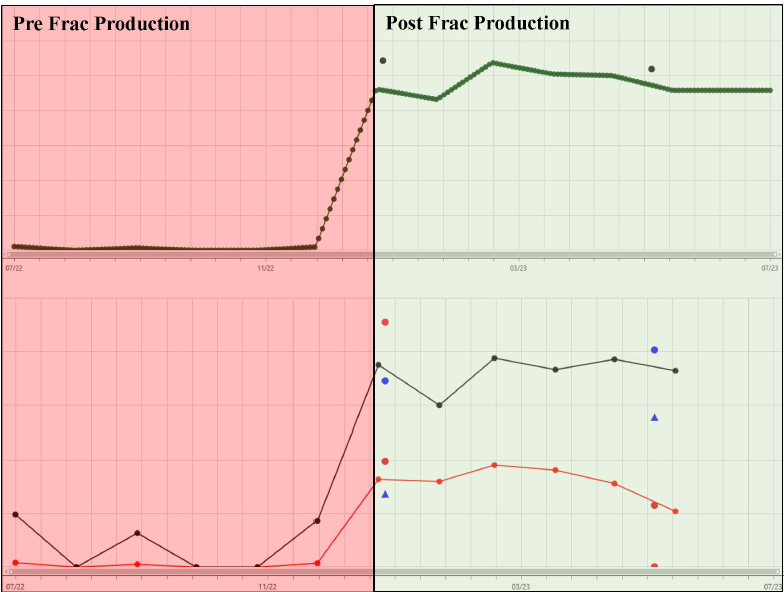
- Substantial improvement in both gross and net oil production (oil production increased by a factor of 20).
- Productivity was sustained, uptime improved from 25% to 100%.
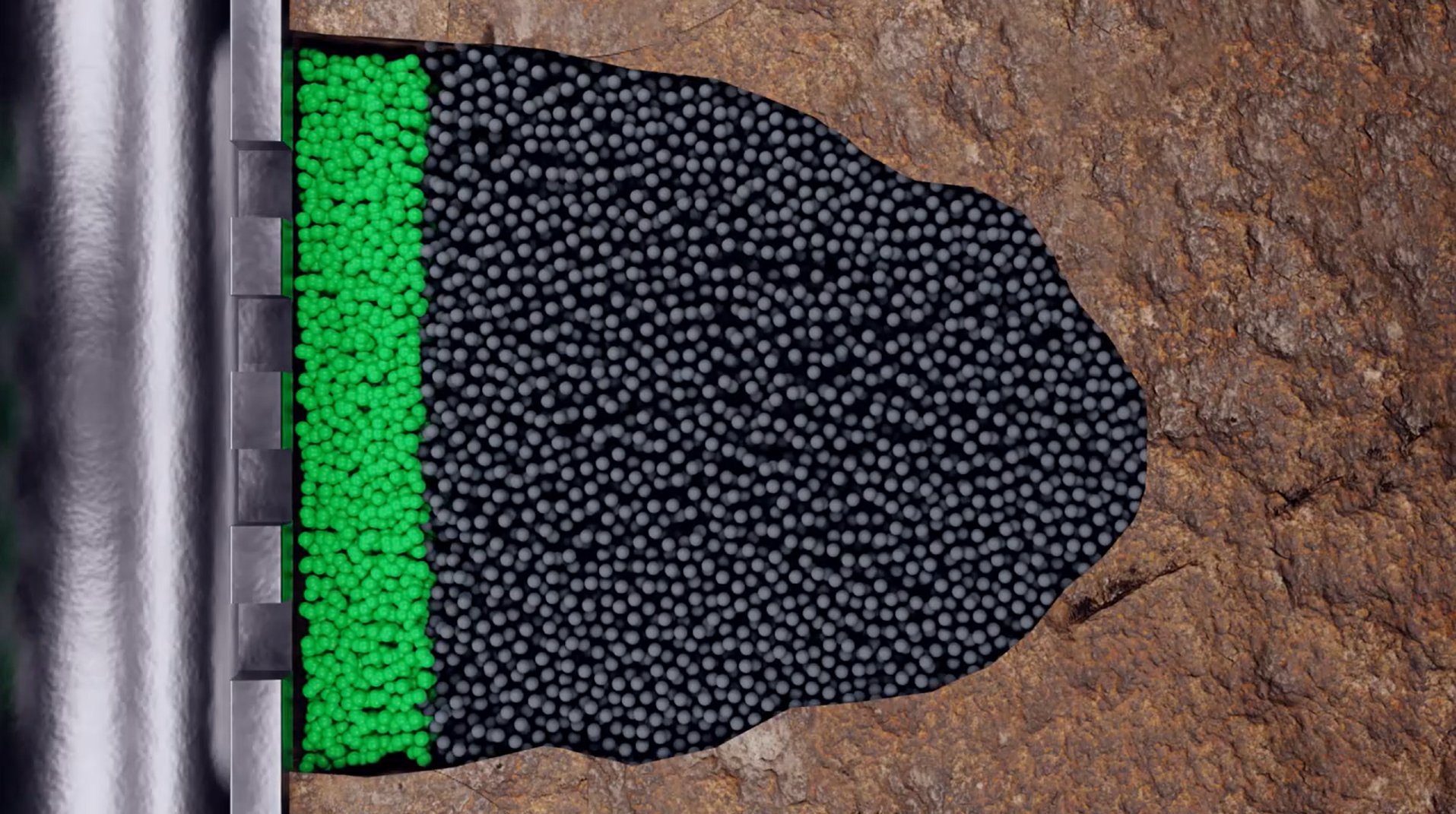
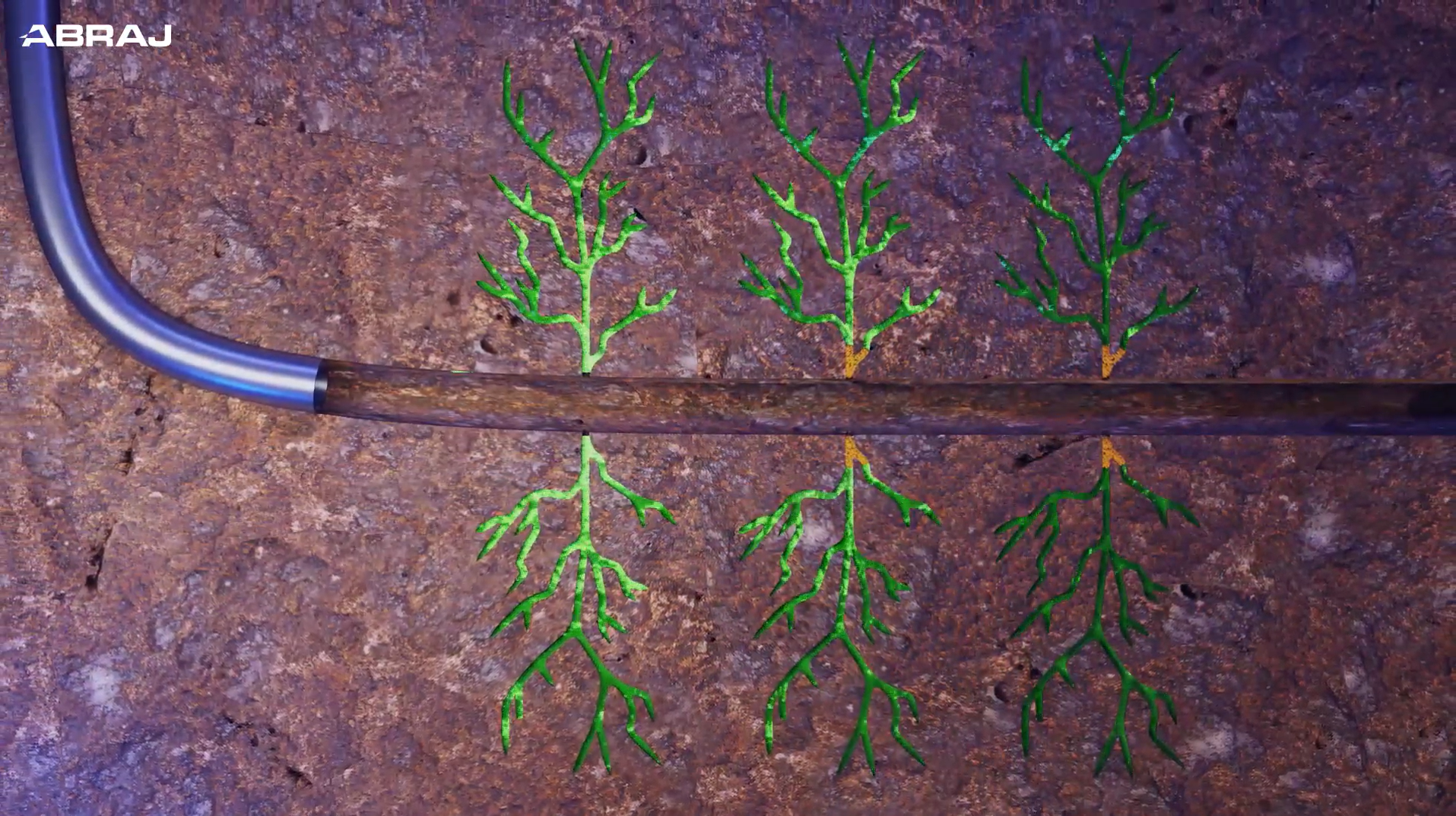
- Propped fracturing method is preferred when applicable, while retarded acid fracturing provide more flexibility for complex pre-existing well completion